Flexible Pavement Design - IES Previous Year Questions
11. A collapsible soil subgrade sample was tested using Standard California Bearing Ratio apparatus and the observations are given below:
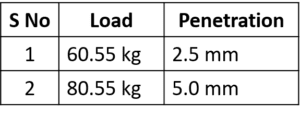
Taking the standard assumptions regarding the load penetration curve, CBR value of the sample will be taken as _____ .
[IES 2016]
- 4.0%
- 4.4%
- 5.5%
- 3.9%
Explanation:
- The load sustained by the standard aggregates at 2.5 mm and 5.0 mm penetration are 1370 kg and 2055 kg respectively.
- CBR of soil subgrade at 2.5 mm penetration =Load sustained by the soil subgrade at 2.5 mm penetration / Load sustained by the standard aggregate at 2.5 mm penetrationx 100%
- CBR of soil subgrade at 5.0 mm penetration =Load sustained by the soil subgrade at 5.0 mm penetration / Load sustained by the standard aggregate at 5.0 mm penetrationx 100%
- Here, CBR 2.5 mm is greater than CBR 5.0 mm. Hence, CBR of the given soil subgrade = 4.4%
12. In the revised CBR design method recommended by the IRC for the design of flexible pavement, the total thickness depends upon _____ .
[IES 2017]
- The CBR value of the soil and magnitude of wheel load.
- The CBR value of the soil and cumulative standard axle loads.
- The CBR value of the soil and number of commercial vehicles passing per day.
- Only the CBR value of the soil.
Explanation:
As per IRC 37:2012, in the design of flexible pavement, the total pavement thickness depends on the cumulative number of standard axles (in Million Standard Axles)to be carried during the design period of the road and the CBR value.
Note: IRC 37:2012 is the latest code in 2017. Check for the latest versions.
13. As per IRC 37:2012, the fatigue life of flexible pavement consisting of granular base and sub-base depends upon
- Resilient Modulus of bituminous layers
- Horizontal tensile strain at the bottom of bituminous layer
- Mix design of bitumen
- Vertical subgrade strain
Which of the above statements are correct ?
[IES 2018]
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 2, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2and 4 only
Explanation:
- Nf = 2.21 x 10-4 x [1/εt]3.89 * [1/M R] 0.854 (80 per cent reliability)
- Nf = 0.711 x 10-4 x [1/εt]3.89 * [1/M R] 0.854 (90 per cent reliability)
Nf - Fatigue life in number of standard axles.
εt - Maximum tensile strain at the bottom of the bituminous layer.
MR - Resilient modulus of the bituminous layer.
14. Consider the following data with respect to the design of flexible pavement:
Design wheel load = 4200 kg, Tyre pressure = 6.0 kg/cm2, Elastic modulus = 150 kg/cm2, Permissible deflection = 0.25 cm. (Take π0.5 = 1.77, π-0.5 = 0.564, 1/π = 0.318 and π2 = 9.87) The total thickness of flexible pavement for a single layer elastic theory will be nearly _____ .
[IES 2019]
- 47 cm
- 51 cm
- 56 cm
- 42 cm
Explanation:
As per single layer elastic theory, the total thickness of the flexible pavement, T = {
Where,
P - Design wheel load = 4200 kg
Es - Elastic modulus of subgrade = 150 kg/cm2
Δ - Permissible deflection = 0.25 cm
a - Radius of contact area
Here, tyre pressure =
⇒
⇒ a = 14.92 cm
Substituting the above values in T, T = 51.35 cm
Here, the closest option is 51 cm.
15. Consider the following statements related to IRC recommendations for the CBR method of design (IRC: 37-1970):
- The CBR tests should be performed on remoulded soils on the field.
- For the design of new roads, the subgrade soil sample should be compacted at OMC to proctor density.
- In new construction, the CBR test samples may be soaked in water for four days period before testing.
Which of the above statements are correct ?
[IES 2022]
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 and 2 only
Explanation:
- CBR tests are carried out on remoulded soil in the laboratory.
- In-situ field tests are not recommended for design purposes.

